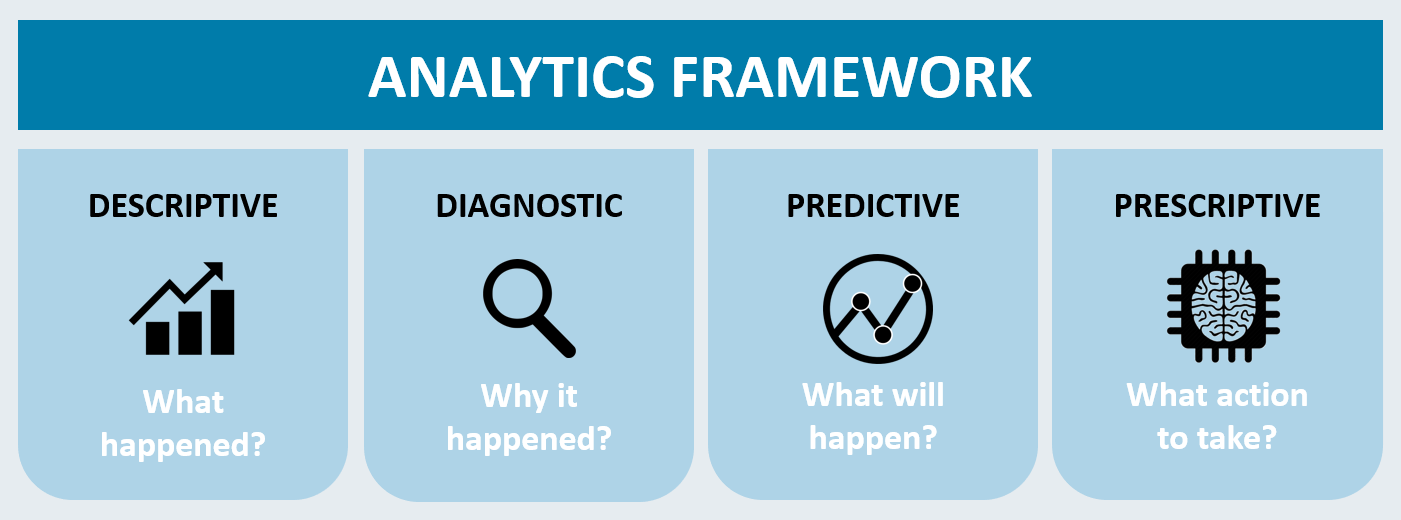
What is Prescriptive Maintenance?
What is Prescriptive Maintenance
Prescriptive maintenance is the asset maintenance strategy that uses machine learning to adjust operating conditions for desired outcomes, as well as intelligently schedule and plan asset maintenance. Prescriptive maintenance not only looks for failure signatures, but also provides information about how to delay or entirely eliminate equipment failure. These algorithms can comb historical data for examples of a wide variety of operating conditions, and also extract patterns and extrapolate data to provide hypothetical operating environments.

It has evolved from predictive. Predictive offers constant monitoring and sometimes a few limited recommendations, and not much else beyond that. Recommendations from predictive maintenance are super relevant to make improvements and avoid unscheduled downtime. But in most cases, they only cover the devices and can’t analyze other variables.
Prescriptive maintenance goes beyond the realm of preventive, descriptive and predictive maintenance. It not only leverages the approach and capabilities of statistical models & forecast techniques but also provides users with the options regarding corrective measures that can be acted upon. With prescriptive maintenance, devices in collaboration with operators are proactive participants in their own maintenance.
When a change in the equipment (the data) occurs, prescriptive maintenance will not only show what and when a failure is going to happen, but why it is happening. Taking it one step further, prescriptive maintenance will take the analysis and determine different options and the potential outcomes to mitigate any risk to the operation.
EXAMPLES OF PRESCRIPTIVE MAINTENANCE
Prescriptive maintenance can be applied to tons of places, but the concept is so new that finding applications in real environments can be challenging. Early adopters mostly use it on a small scale and usually outside the process automation world. So far, we’re only seeing it in parts of processes instead of throughout entire runs. However, those segments can provide pieces of the performance picture by measuring certain points, then analyzing the data gathered.
BARRIERS TO PRESCRIPTIVE MAINTENANCE
- Cost– Along with the hardware and software cost, there will be some learning costs that are incurred when organizations are still using traditional maintenance techniques while prescriptive maintenance is being tested and validated.
- Regulations – certain regulations may not allow the traditional maintenance approach to fade into the past. As a result, prescriptive maintenance may not be allowed in place of traditional maintenance activities when dealing with regulatory bodies.
- Culture – There may be significant hurdles to overcome with the company culture to implement prescriptive maintenance. Predictive maintenance sounds great – maintain your assets, before they show outward signs of failure and cause unplanned downtime (loss of revenue), whilst spending less money than you would for a preventative maintenance program – boosting profitability and throughput.
Prescriptive Maintenance is the future of maintenance.







Leave a Comment