How optimizing Asset operations can save you huge costs?
Asset Management System
Asset management is the process of considering the commissioning, operational, and end-of-life phases of physical assets. However, current asset management models show inefficiencies in
terms of addressing life cycle cost comprehensively.
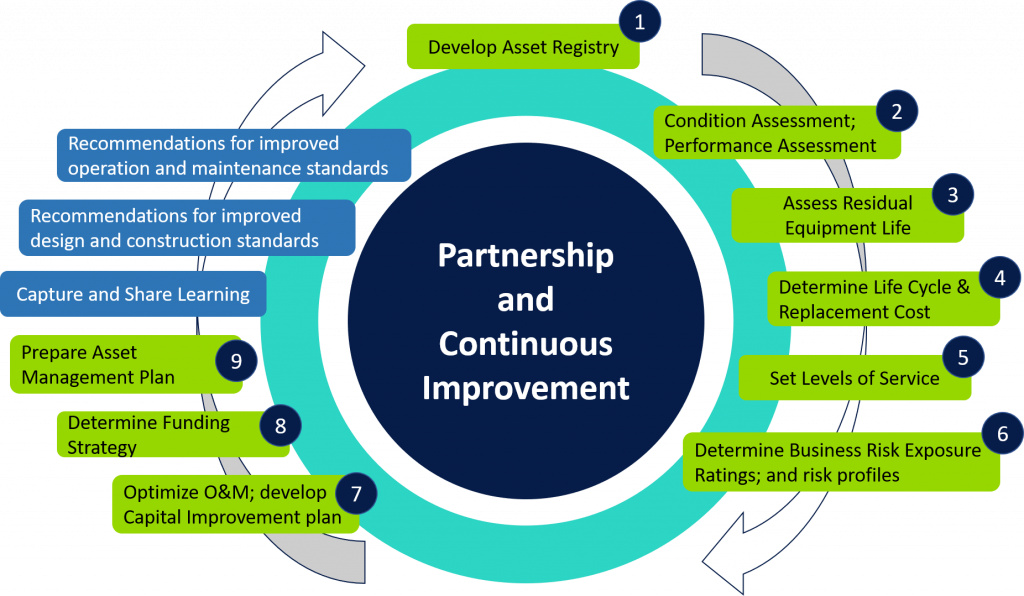
Following are the major steps:
- Asset registry: Record the details like make, model, current status, location, condition, etc. This information is compiled for all the assets with a unique id. Watch a video here.
- Asset hierarchy: Establish a parent-child relationship between the assets to correctly maintain a cause and effect knowledge and to better organize the part and sub-parts.
- Preventive maintenance: Schedules are prepared for planned tasks with the frequency of tasks to be performed on the assets along with the checklists.
- Breakdown maintenance: Reactive maintenance is recorded with the job details, nature, and extent of faults.
Usually, assumptions are made to determine the maintenance cost at an early stage, and
maintenance cost benchmarks can be used, such as maintenance cost as a percentage of
equipment replacement value. If it is found that it may not be cost-effective to operate specific equipment within the expected reliability parameters, alternative solutions should be considered. Trade-offs between initial capital expenditure and operation and maintenance costs should be analyzed
and the best solution selected.
Asset Maintenance System
How can we attain a great asset management system?
With the use of technology, things which were previously not feasible like real-time recording and extraction of data are now possible, provided the system is easy to use and proper training is done for the staff.
- Recording, browsing, and fetching the information with a digital asset registry system helps in bringing more control on the assets. Critical alerts based on the daily transactional work orders and inventory movement can be expected.
- The main objective is to extend the asset life so a good digital system can ensure that a PM schedule is not missed and if missed it should be escalated instantly. Also, It should address the issue of scale and should be able to work correctly in a complex environment where thousands of assets with defined interoperability are there.
- The events of breakdown should be handled very intelligently by the system. consider a scenario in which a particular part is getting defected after the lubricating oil from a different vendor was used. Previously it was working fine. So in this case a system must be able to relate the even of changing the brand of oil with increased failure. There are lot many such scenarios where a correct and detailed recording of a breakdown even should be entered and a proper algorithm should be run to get the desired information that could help in decision-making.
So, a CMMS/CAFM solution if implemented thoroughly with great stress on maintenance staff training then the asset lifecycle cost is greatly reduced and operations are optimized.
Contact Now to Digitize your Asset Maintenance.











Leave a Comment