What is Facility Management Software – A Complete Guide
Caught in a chaotic web of reactive maintenance and siloed data? Now, picture your facilities humming with optimized workflows, work orders flowing like a well-choreographed ballet, and data singing its siren song of actionable insights. Facility management software makes it real by weaving a tapestry of efficiency and insight.
What is Facility Management Software-A Complete Guide
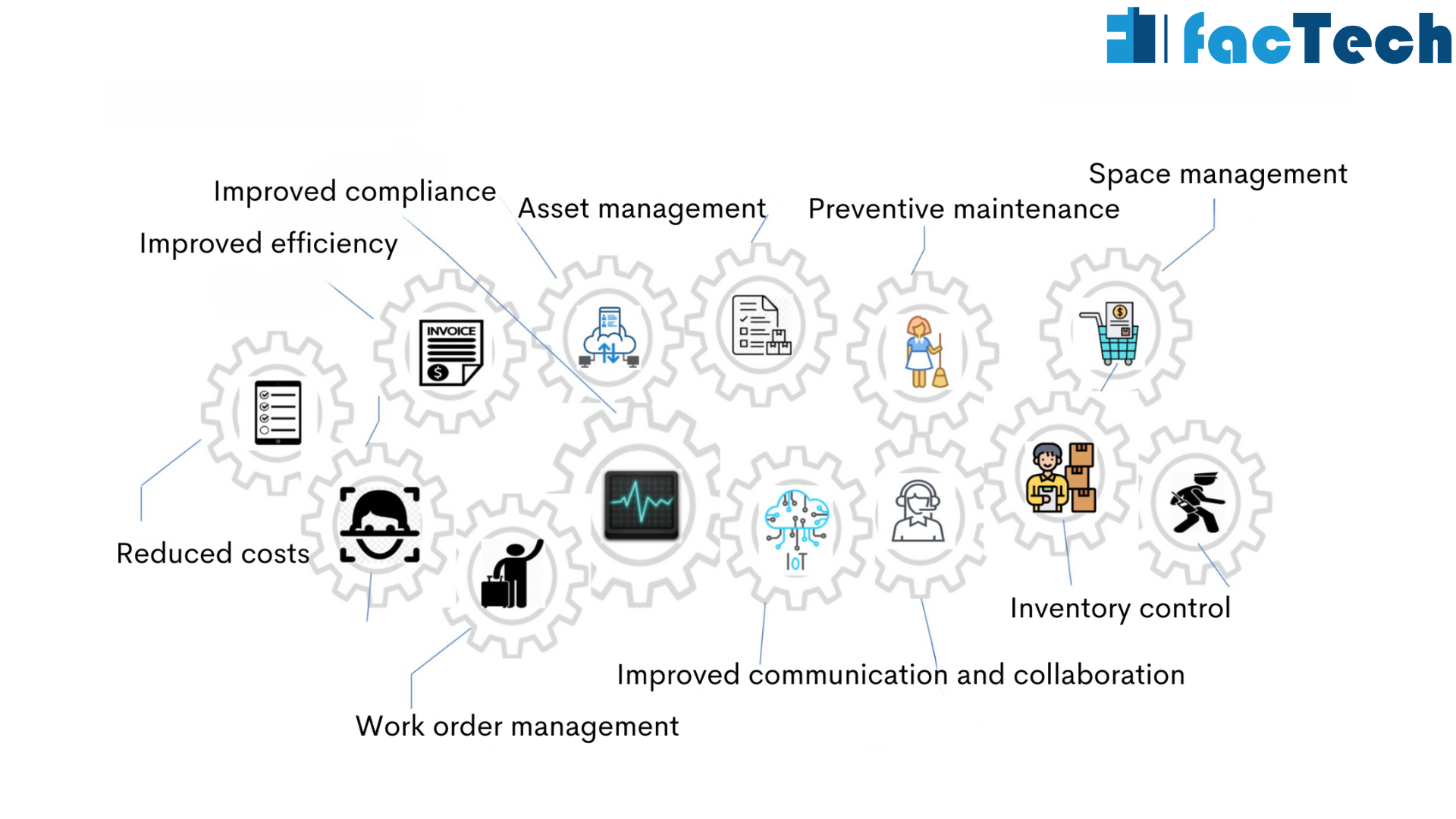
Facility management software (or facility management system) is a digital tool that helps organizations optimize their facility operations. It’s like a digital command center for your buildings, providing a centralized platform to manage everything from work orders and preventive maintenance to inventory control and space utilization.
What Does Facility Management Software Do?
Harnessing the power of FMIS, FMS offers a wide range of features and functionalities, but some of the core capabilities include:
1. Work order management:
In facility management software, work order management is a crucial component that streamlines the process of handling maintenance requests and tasks within a facility. It acts as a central hub for creating, assigning, tracking, and completing work orders, ensuring smooth upkeep and operation of your facilities.
Here’s how it works:
Creating Work Orders:
Streamlining facility management, the software acts as a central hub for both users and managers. Facility users, whether staff, tenants, or any other stakeholder, can submit requests for various services through multiple convenient channels like mobile apps, web portals, or even email. These requests capture crucial details like the type of request, specific location within the facility, urgency level, and even a desired completion date, ensuring clarity and context for efficient resolution. Additionally, facility managers can leverage the software’s automation capabilities to generate preventive maintenance work orders based on pre-defined schedules, proactively addressing potential issues before they arise. This comprehensive approach empowers both users and managers, creating a smooth and efficient facility management experience.
Assigning and Scheduling:
Streamlining efficiency, the software prioritizes tasks based on urgency, impact, and available resources. Skilled technicians with the right tools are matched to work orders, ensuring optimal execution. To achieve this, the system generates intelligent work schedules that consider technician availability, potential task overlaps, and critical deadlines, guaranteeing smooth operations and timely completion.
How to assign Work Order/ Schedules to Team in Kaizen CAFM
Tracking and Completion:
Streamlining efficiency, the software prioritizes tasks based on urgency, impact, and available resources. Skilled technicians with the right tools are matched to work orders, ensuring optimal execution. To achieve this, the system generates intelligent work schedules that consider technician availability, potential task overlaps, and critical deadlines, guaranteeing smooth operations and timely completion.
2. Preventive maintenance:
Sure! Preventive maintenance (PM) is a crucial strategy within facility management software, aiming to prevent equipment failures and breakdowns before they occur. It involves routinely inspecting, cleaning, lubricating, and replacing parts of facilities and equipment to maintain their optimal performance and lifespan.
Here’s how preventive maintenance works in conjunction with facility management software:
Scheduling and Tracking:
Automated Schedules: Facility managers can define PM tasks and set up recurring schedules within the software. This ensures tasks are completed on time, preventing potential issues from arising.
How to assign Work Order/ Schedules to Team in Kaizen CAFM
3. Asset management:

Asset management in FMS refers to the process of tracking, maintaining, and optimizing the physical assets of a facility. This includes tasks such as:
Creating an asset inventory: This involves creating a record of all assets in the facility, including their location, condition, and value.
Tracking asset lifecycles: This involves tracking the lifecycle of each asset, from acquisition to disposal.
Scheduling preventive maintenance: This involves scheduling regular maintenance tasks for assets to prevent breakdowns and extend their lifespan.
Managing repairs and replacements: This involves managing the repair and replacement of assets when they break down or reach the end of their useful life.
Optimizing asset utilization: This involves making sure that assets are used efficiently and effectively.
4. Inventory control:
Inventory control in facility management software refers to the tools and functionalities that enable organizations to track, manage, and optimize their stock of various items, including:
Maintenance supplies: Spare parts, tools, cleaning materials, etc.
Office supplies: Stationery, printer cartridges, etc.
Safety equipment: Personal protective equipment (PPE), first-aid kits, etc.
Janitorial supplies: Cleaning products, paper towels, trash bags, etc.
Key Features of Inventory Control in Facility Management Software:
Item cataloging: Create and manage a detailed catalog of all inventory items, including descriptions, part numbers, and images.
Stock level tracking: Track real-time inventory levels for each item, preventing stockouts and overstocking.
Low-stock alerts: Set up automated alerts to notify you when stock levels reach predefined thresholds, triggering timely reordering.
Purchase order management: Generate and manage purchase orders for suppliers, streamlining the procurement process.
Location tracking: Assign locations to inventory items, ensuring easy retrieval and preventing loss.
Reporting and analytics: Generate reports on inventory usage, reorder points, and supplier performance, providing valuable insights for optimization.
Barcode scanning: Utilize barcode scanners for faster and more accurate inventory counts and transactions.
Integration with other modules: Integrate inventory control with other modules like work order management and preventive maintenance for a holistic view of resource utilization.
5. Space management:

Space management is a crucial aspect of facility management, and facility management software (FMS) plays a vital role in streamlining and optimizing this process. It helps organizations effectively track, allocate, and utilize their physical space, leading to increased efficiency, cost savings, and employee satisfaction.
Key Features of Space Management in FMS:
Floor plan visualization: FMS provides visual representations of floor plans, allowing users to see the layout of their facilities, including individual rooms, equipment, and furniture. This visual representation memudahkan space allocation, planning, and optimization.
Space inventory management: The software tracks and maintains a comprehensive inventory of all spaces within a facility, including their size, type (e.g., office, conference room, break room), capacity, and current occupants. This data is essential for informed decision-making regarding space allocation and utilization.
Space utilization tracking: FMS monitors how space is being used in real-time, often through sensors or occupancy management systems. This data helps identify underutilized spaces and optimize space allocation to create a more efficient and cost-effective work environment.
Space reservation and scheduling: The software allows users to reserve specific spaces for meetings, events, or individual use. This helps avoid conflicts and ensures that everyone has the space they need when they need it.
Space planning and modeling: Some advanced FMS solutions offer space planning and modeling tools that allow users to virtually test different layout configurations and see how they would impact space utilization, employee workflow, and overall efficiency.
6. Reporting and analytics:
In the complex world of facility management, data is king. But raw data alone isn’t enough. To truly optimize your operations, you need tools to transform that data into actionable insights. That’s where reporting and analytics capabilities in facility management software come in.
What are Key Performance Indicators (KPI) in Facility Management?
What it does:
Reporting and analytics in FMS provides a comprehensive view of your facilities, enabling you to:
Track Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Monitor metrics like maintenance costs, space utilization, energy consumption, and service request response times.
Identify Trends and Patterns: Analyze historical data to uncover trends and patterns, helping you predict future needs and potential issues.
Benchmark Performance: Compare your facility’s performance against industry standards or internal benchmarks to identify areas for improvement.
Make Data-Driven Decisions: Use insights to inform strategic decisions about maintenance schedules, resource allocation, space optimization, and more.
Key Features:
Customizable Reports: Create reports tailored to your specific needs, focusing on relevant KPIs and timeframes.
Dashboards and Visualizations: Present data in clear, easy-to-understand formats like charts, graphs, and maps for quick insights.
Drill-Down Capability: Explore data deeper by drilling down into specific areas for more granular analysis.
Alerting and Notifications: Get notified about critical events or performance deviations requiring immediate attention.
Integration with Other Systems: Integrate with other software, like work order management and asset management, for a holistic view.
Benefits of Using Facility Management Software
The amount of benefits are immense so let’s check out few of them:
1. Efficiency Boost:
Streamlined Workflows:
Eliminate manual tasks like paper-based work orders and endless email chains. FMS centralizes everything, from work order creation to completion, with real-time updates and tracking.
Automated Processes:
Schedule preventive maintenance, generate automated reports, and trigger notifications for critical events, freeing up valuable time and ensuring tasks don’t slip through the cracks.
Improved Communication:
Break down silos between departments and contractors with a central platform for communication and collaboration, leading to faster resolution times and smoother operations.
2. Cost Savings:
Reduced Maintenance Costs:
Preventative maintenance plans driven by FMS data minimize equipment breakdowns and extend asset life, saving on expensive repairs and replacements.
Optimized Resource Allocation:
Track and analyze data to identify areas for resource optimization, allowing you to deploy staff and technicians strategically for maximum efficiency.
Lower Energy Consumption:
Monitor and analyze energy usage and identify areas for improvement, leading to reduced utility bills and a more sustainable footprint.
3. Enhanced Decision-Making:
Data-Driven Insights:
Transform raw data into actionable reports and dashboards, providing clear visibility into facility performance. Use these insights to make informed decisions about space utilization, maintenance schedules, and budget allocation.
Trend Analysis:
Identify trends and patterns in historical data to predict future needs and proactively address potential issues before they escalate.
Benchmarking:
Compare your facility’s performance against industry standards or internal benchmarks to identify areas for improvement and track progress over time.
4. Improved Safety and Compliance:
Centralized Documentation:
Store safety procedures, maintenance logs, and compliance certificates in one secure location, ensuring easy access and streamlined audits.
Proactive Risk Management:
Track safety incidents and identify potential hazards, allowing you to implement preventive measures and create a safer work environment.
Automated Compliance Reports:
Generate reports demonstrating compliance with regulations, simplifying the process and reducing the risk of fines.
5. Increased Tenant Satisfaction:

Enhanced Service Delivery:
Offer tenants self-service portals for reporting issues and tracking work order progress, leading to faster response times and improved satisfaction.
Space Optimization:
Analyze space utilization data to create a more efficient and comfortable work environment for tenants, boosting their productivity and satisfaction.
Improved Communication:
Keep tenants informed about facility updates, maintenance schedules, and any potential disruptions through centralized communication channels.
Conclusion
FM Software is a valuable tool that can help organizations improve their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and comply with regulations. If you’re looking for ways to improve your facility management, consider investing in a facility management software solution.
Contact us for a free demo of how our expertise can help you achieve your business goals to the best.